Decentralised Finance, or DeFi, is an emerging industry that uses blockchain technology and cryptocurrency to create decentralised financial services such as payments, loans and insurance. DeFi services aren’t owned or controlled by a centralised authority and have no middlemen. DeFi can help deliver affordable financial services to low-income people and can simplify the complicated financial systems used to transfer money globally today.
Because DeFi represents such a radical change from the way it delivers financial services today, it’s unclear how governments might try to regulate and control it in the future.
Society today is organised in a hierarchy. The world is divided into countries, and each country has a centralised government that controls it. A government typically issues a currency and maintains a centralised bank to regulate the supply and demand of the currency. Beneath the central bank in the hierarchy are other large, centralised financial institutions such as banks and credit unions.
The large financial institutions have a great deal of power and influence because they decide what kinds of financial products and services to offer, who can use them and how much they cost.
For example, banks offer different credit cards. The bank decides if you can have a card, which card you can have, and what interest rate you pay. Unfortunately, large, centralised financial institutions are also susceptible to greed, corruption and fraud that can have devastating effects on the global economy.
Bitcoin and blockchain technology prove that there is an alternative way to make payments from one person to another without relying on any centralised third party like a bank or credit card company. Bitcoin is not issued by a government, and the blockchain is not controlled or owned by a centralised authority or government. For these reasons, Bitcoin is regarded as decentralised money.
More Than Payments
Making payments is only one small part of the broader financial services industry. However, just as Bitcoin decentralises money, it’s now possible to decentralise other financial services. Using blockchain technology and cryptocurrency, you can create exchanges, savings, loan and insurance services that decentralise control. These services enable peer-to-peer transactions, don’t require a third-party intermediary, and have no owner or entity that controls them. Collectively, the decentralised financial services comprise Decentralised Finance, or DeFi.
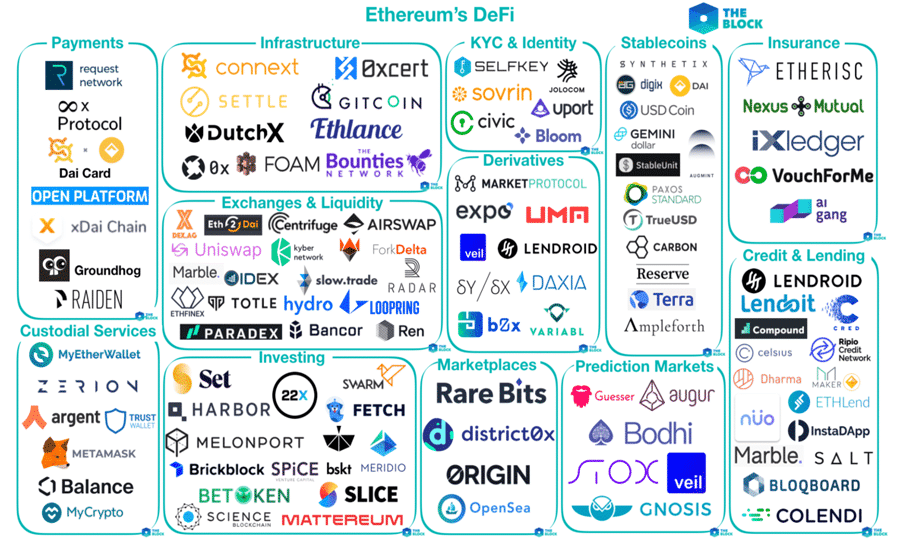
The Ethereum blockchain is the most popular platform today for DeFi services. Ethereum supports the ability to program terms, conditions and actions into “smart contracts” that run automatically without human intervention.
DeFi services are typically delivered as Decentralised Applications, or dApps. A dApp can provide a simple service such as converting from one cryptocurrency to another or a complex platform that connects lenders and borrowers. Developers can create new financial service offerings by connecting different dApps together like Lego building blocks.
The Future of DeFi and Fintech
DeFi represents the cutting edge of innovation in financial services technology, or Fintech. Because it is decentralised and automated, DeFi can potentially deliver affordable financial services to about 25 percent of the world’s population who today have no bank account or no access to any financial services.
While DeFi inherits its strong security and transparency from the blockchain technology that powers it, it also has risks. The technology and entire industry are new and errors in smart contract programming have enabled attackers to exploit holes in the rules and steal money. It’s also unclear how governments around the world will try to regulate or control DeFi services.
It’s an exciting, but risky time to be involved with DeFi. As always, make sure you do your own research and due diligence – and above all, understand basic computer safety. You can check out our basic security tips here.


